| Traditional Model | KEYPACK Intelligent Early Warning System |
| Just detecting parameters, fault alarms. Examples: pump overclocking, elevated conductivity alarms, etc. | Automatic early warning judgment (trend analysis, cumulative value statistics). |
| It's only when there's an actual malfunction that the alarm goes off. | Be proactive and alert before an overrun/failure actually occurs, reducing the risk of downtime. |
| The same fault may be caused by a variety of reasons, the traditional way can not directly identify the fault (specific points) need to be investigated one by one, more dependent on "experience" judgment. | Quickly identifies the actual problem point when a failure occurs, along with the solution, eliminating the need to spend a lot of time analyzing the problem point. |
| Spare parts/consumables, purchased and replaced based on "experience". | Spare parts/consumables are managed based on "data" and purchases and replacements are justified. |
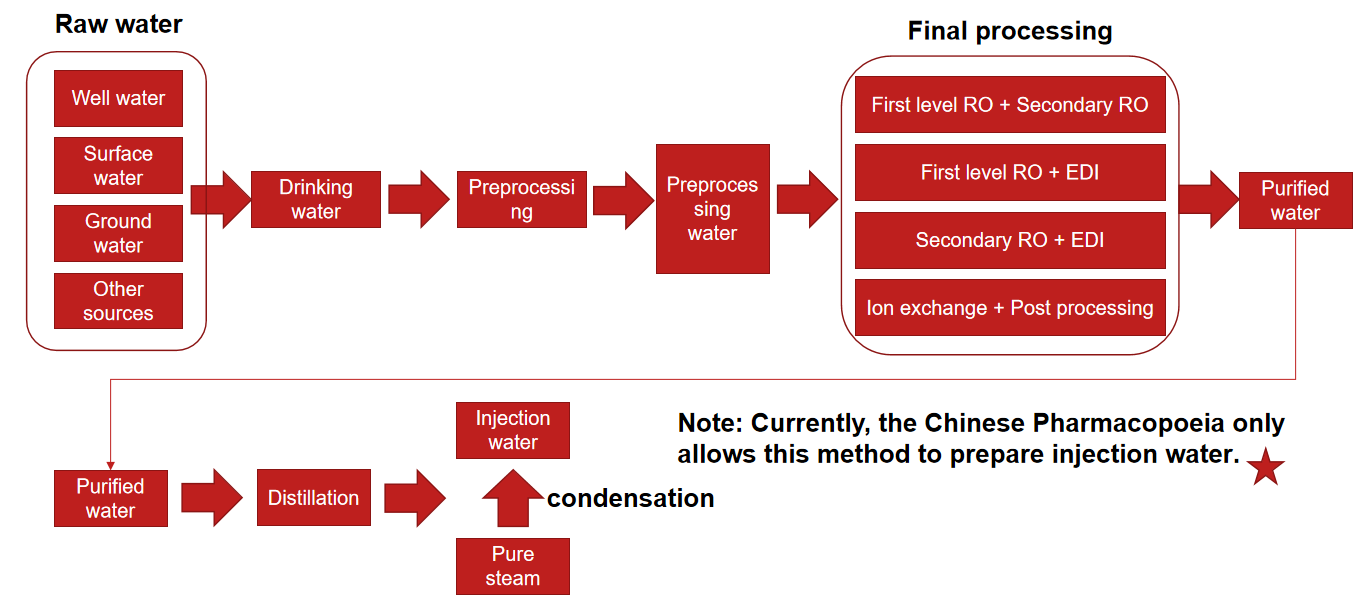
Meets various regulatory requirements
| Country | Standard System |
| WHO World Health Organization | WHO World Health Organization |
| China | Good Manufacturing Practice and its appendices Guide to Pharmaceutical GMP: Plant Facilities and Equipment Chinese Pharmacopoeia, abbreviated CP |
| European Union (EU) | Guideline on the quality of water for pharmaceutical use EU GMP Appendix 1 Aseptic Product Production European Pharmacopoeia, abbreviated EP |
| United States | High Pure Water System Inspection Guide |